
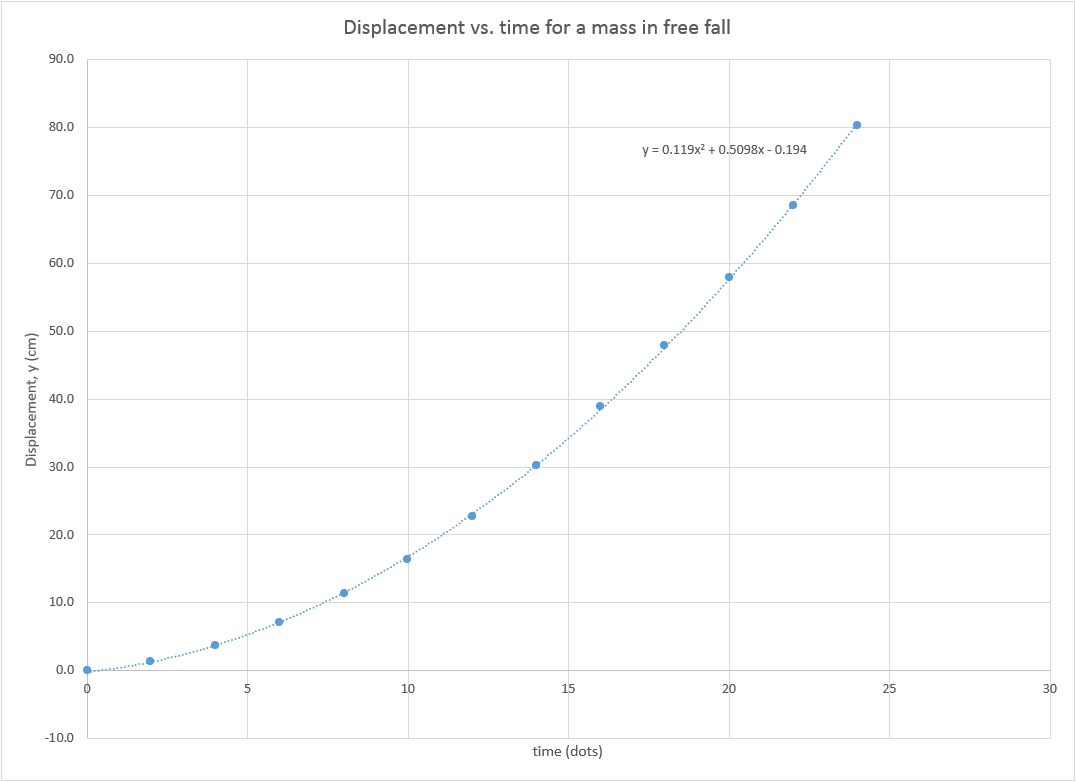
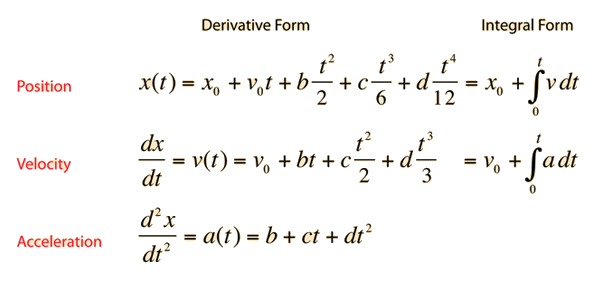
The displacement (d) of the shingles is -8.52 m. You might note that in the statement of the problem, there is only one piece of numerical information explicitly stated: 8.52 meters. The second step involves the identification and listing of known information in variable form. The solution to this problem begins by the construction of an informative diagram of the physical situation. That is, a ball projected vertically with an upward velocity of +30 m/s will have a downward velocity of -30 m/s when it returns to the same heightġ. This value can be used as one of the motion parameters in the kinematic equations for example, the final velocity (vf) after traveling to the peak would be assigned a value of 0 m/s.Ĥ.If an object is projected upwards in a perfectly vertical direction, then the velocity at which it is projected is equal in magnitude and opposite in sign to the velocity that it has when it returns to the same height. The instant at which it reaches the peak of its trajectory, its velocity is 0 m/s. (The - sign indicates a downward acceleration.) Whether explicitly stated or not, the value of the acceleration in the kinematic equations is -9.8 m/s/s for any freely falling object.Ģ.If an object is merely dropped (as opposed to being thrown) from an elevated height, then the initial velocity of the object is 0 m/s.ģ.If an object is projected upwards in a perfectly vertical direction, then it will slow down as it rises upward.
#Freefall position physics free
1.An object in free fall experiences an acceleration of -9.8 m/s/s.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
